Art Clomera
Vice President, Operations
The AI RMF is an extension of the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF), tailored for artificial intelligence (AI) systems. It provides organizations with a structured approach to identify, assess and manage risks related to AI technologies throughout their lifecycle.
The new battlefield is dominated by software and hardware. To navigate this terrain, the NIST AI RMF 1.0 serves as a strategic guide, helping to manage the challenges presented by the rapid evolution of AI and its impact on security. As cybersecurity professionals, we embrace new technologies that help defend federal networks against attacks. AI is emerging as an indispensable tool in this effort. Unfortunately, the horizon is not without its shadows. AI introduces widespread risks from privacy violations and security breaches to ethical concerns. Because it is a Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), the list is long and daunting. It’s why the AI RMF is such an achievement.
What is the NIST AI RMF 1.0?
NIST AI RMF 1.0 was released in January 2023, following on the heels of the Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP). With the rise of Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), we have seen that AI has profound economic and societal consequences. According to NIST, AI risk is unique because it can impact people, organizations, and entire ecosystems. So, the framework considers the social, economic, and human factors that can impact the development and use of AI systems.
The AI RMF identifies 14 unique AI risks distinct from traditional privacy and cybersecurity issues, making it the AI-specific (gold) standard of care and standardized controls. Its release adds coherence to U.S. policy on AI and contributes to the global debate on AI policy and development. Here is a table summarizing the different types of AI risk and how they can impact people, organizations, and ecosystems:

Four Core Functions Included in the NIST AI RMF Playbook
The NIST AI RMF Playbook is a valuable resource for organizations dedicated to developing trustworthy and responsible AI systems. It provides a framework for AI risk management and assessment, flexible enough to be adapted to the specific needs of different organizations. With technology advancing rapidly, a new tactical map to manage and assess the risks AI poses to our networks, our organizations, and our communities could not have come sooner.
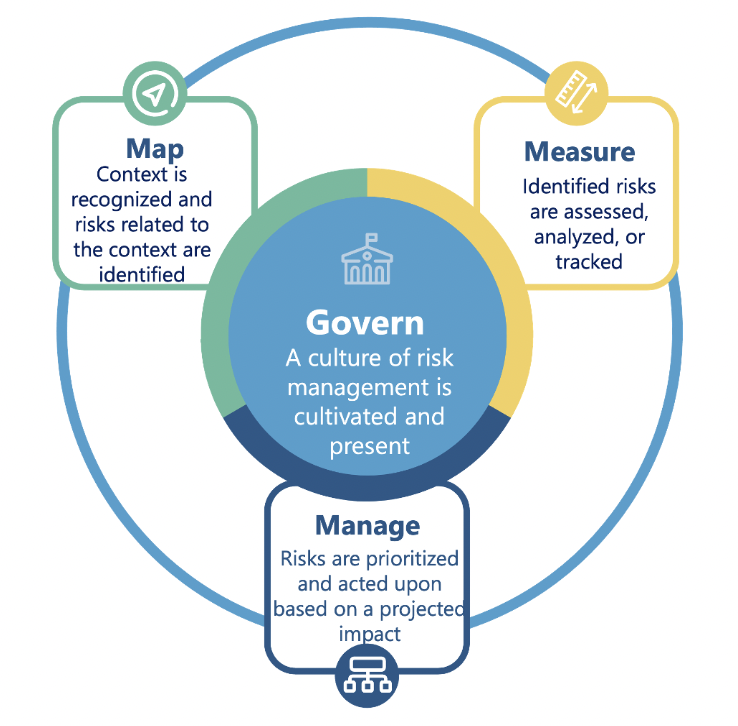
Govern
GOVERN recognizes AI’s evolving legal and regulatory landscape and emphasizes the need for organizations to assess relevant laws and regulations. By doing so, they can mitigate legal risks and ensure the responsible and lawful use of AI technologies.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Artificial Intelligence (AI) Risk Management Framework (AI RMF). Source
Additionally, the function acknowledges that organizations have different risk tolerances for AI. GOVERN helps organizations determine risk tolerance levels and develop a tailored AI risk management approach.
GOVERN is essential because it promotes responsible AI development, compliance with laws, and effective mitigation of AI risks.
Map
The MAP function in the NIST AI RMF playbook provides a structured approach to building an organization’s socio-technical footing. By utilizing an internal interdisciplinary team, identifying potential impacts, and avoiding blind spots, organizations can ensure that AI development and deployment align with complex social, economic, and cultural contexts.
By mapping potential impacts early, By mapping potential impacts early, MAP encourages interdisciplinary expertise by forming diverse teams from various fields, such as data science, ethics, law, and social sciences by mapping potential impacts early. This collaborative approach helps organizations understand AI systems’ multifaceted impacts and risks, aiding in informed decision-making. By mapping potential impacts early, organizations can proactively identify and address risks such as unintended consequences, biases, privacy concerns, and ethical issues.
MAP enables a thorough AI risk assessment, and considering diverse perspectives prevents blind spots in understanding the risk and impact of AI systems.
Measure
MEASURE helps organizations focus on evaluating the trustworthy characteristics of the risks that were mapped out. By measuring these trustworthy characteristics, organizations can gauge the risk associated with each characteristic and prioritize mitigation efforts accordingly. This helps ensure that AI systems meet the desired level of trustworthiness and align with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. The NIST AI RMF identifies seven trustworthy characteristics of risks:
- Valid and Reliable
- Safe
- Secure and Resilient
- Accountable and Transparent
- Explainable and Interpretable
- Privacy-Enhanced
- Fairness – With Harmful Bias Managed
Manage
After the trustworthiness characteristics of an AI system have been measured, MANAGE lays out a framework for organizations to make trustworthiness an ongoing and evolving process of their AI systems.
Firstly it advises collecting and analyzing data to detect deviations and risks. After monitoring the results, iterative improvements can be made by updating policies, procedures, and technical components. Next, actively seek stakeholder feedback to address concerns and incorporate valuable insights. Finally, document all monitoring activities, improvements, and stakeholder engagement as a record of responsible AI development; this will ensure compliance, transparency, and accountability.
Eight Key Takeaways and How it Relates to the Broader AI Governance Landscape
The NIST AI RMF embeds trustworthiness characteristics into AI systems. It allows Government agencies to develop responsible AI practices, address emerging challenges, and maintain trust in their AI systems by prioritizing trustworthiness characteristics and adopting comprehensive risk management practices.
1. Governance is the backbone of AI RMF
Governance serves as the foundation of the AI RMF. It provides crucial structure, guidelines, and procedures that govern the creation and implementation of AI systems. By establishing comprehensive governance frameworks, organizations can ensure their AI systems comply with ethical norms, legal mandates, and societal values. Effective governance encourages teamwork, defines responsibilities, and aids decision-making. It allows Federal agencies to manage the intricacies of AI governance and develop reliable AI systems for societal good.
2. Trustworthiness characteristics
Trustworthy AI is pivotal in developing and deploying AI systems. The NIST AI RMF highlights seven characteristics of trustworthiness: accuracy, explainability, privacy, reliability, safety, security, bias mitigation, fairness, and transparency. These characteristics ensure that AI systems operate with integrity, accountability, and ethical considerations, fostering trust among users and stakeholders. By prioritizing these trustworthiness characteristics, organizations can build AI systems that are responsible, reliable, and aligned with societal values.
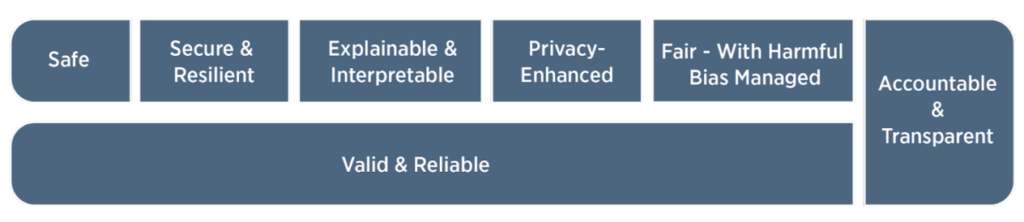 Figure 4: Characteristics of trustworthy AI systems. Valid & reliable is a necessary condition of trustworthiness and is shown as the base for other trustworthiness characteristics. accountable & transparent is shown as a vertical box because it relates to all other characteristics. Source
Figure 4: Characteristics of trustworthy AI systems. Valid & reliable is a necessary condition of trustworthiness and is shown as the base for other trustworthiness characteristics. accountable & transparent is shown as a vertical box because it relates to all other characteristics. Source
3. Socio-Technical Risks: Security, Safety, Privacy and Bias.
Managing bias in AI systems is crucial for establishing and maintaining trust in their operation. Bias remains prevalent in AI systems across various domains, leading to harmful impacts regardless of intent. A socio-technical approach to testing, evaluation, verification, and validation (TEVV) is recommended. TEVV connects the technology to societal values and aims to develop recommended practices for deploying AI/ML-based decision-making applications.
4. Challenges: Risk Measurement; Risk Tolerance; Risk Prioritization,
Measuring risk becomes complex, as it can vary significantly across different entities, making a one-size-fits-all approach impractical. Similarly, risk tolerance varies, with each organization having its threshold for acceptable risk levels. Further complicating matters is the task of risk prioritization; the diversity of potential AI risks and differing organizational priorities can make this a daunting task. NIST recognizes these complexities and underscores the need for organizations to tailor their risk management strategies, aligning them with their specific needs and contexts for a more effective approach.
5. The Future of AI in RMF
Unlike the EU’s regulatory and legal approach to AI risk management, the AI RMF is a voluntary and flexible tool for organizations that want to manage the risks of AI. It will be used by a broader range of organizations, including those in the private sector, public sector, and academia. The future of AI RMF is promising, as Version 1 will receive iterative updates, evolving at the pace of AI’s associated risks.
6. Keep AI RMF aligned with other published documents AI & Cybersecurity
Alignment enhances the effectiveness and usability of the NIST AI RMF, making it easier for organizations to implement and apply in their AI risk management practices. By aligning with other resources, the AI RMF promotes the safe and secure use of AI systems, fostering trust and reliability in the AI landscape. Here are some of the documents that the AI RMF should be aligned with:
- NIST Special Publication 800-53, Revision 5: This document provides comprehensive security controls to protect information systems and organizations.
- NIST Special Publication 800-30, Revision 1: This document provides a risk management framework to assess and manage the risks associated with information systems.
- NIST Special Publication 800-137, This document guides the application of security and privacy principles to machine learning (ML) systems.
7. Operationalize AI RMF into specific sectors
Operationalizing the NIST AI RMF into specific sectors is key to implementation. This involves customizing the framework to meet the unique needs of organizations within different industries. By creating profiles, organizations can apply the AI RMF to address sector-specific risks and challenges. This process allows organizations to align their existing risk management practices with the AI RMF, ensuring a comprehensive approach to AI risk management within their sector.
8. The NIST AI RMF offers several benefits in the long term:
- Protecting against reputational harm: By addressing risks and ensuring the responsible use of AI systems, organizations can protect their reputation and reduce the potential harm associated with biased, insecure, or privacy-invading AI technologies.
- Aligning practices with principles: The framework aligns with fairness, transparency, accountability, and robustness, allowing organizations to demonstrate their commitment to ethical AI and build trust with stakeholders.
- Community information sharing: The NIST AI RMF encourages knowledge sharing and collaboration among organizations, fostering a community of practice that enables learning, improvement, and the advancement of AI risk management as a collective effort.
- Improving interoperability: The framework promotes a common language and principles, enhancing interoperability between different AI systems. This facilitates the coordinated and effective use of AI technologies across organizations and sectors.
Wrapping Up
In April, Senator Warner highlighted concerns about data supply chain security and data poisoning attacks in AI systems. AI’s unique security concerns also include complex algorithms leading to hidden flaws, novel threats beyond traditional ones, and challenges to how information privacy has historically operated. Federal agencies must understand these risks and implement robust measures to mitigate them.
With IPKeys CLaaS, a standards-based approach to NIST RMF, Federal agencies can reduce the costs of their cybersecurity programs by increasing efficiency and improving accuracy through DoD-inspired, AI-powered solutions. Talk to us about jumpstarting your organization’s cybersecurity program.
AI in RMF – Common FAQs
How is RMF AI used in risk management?
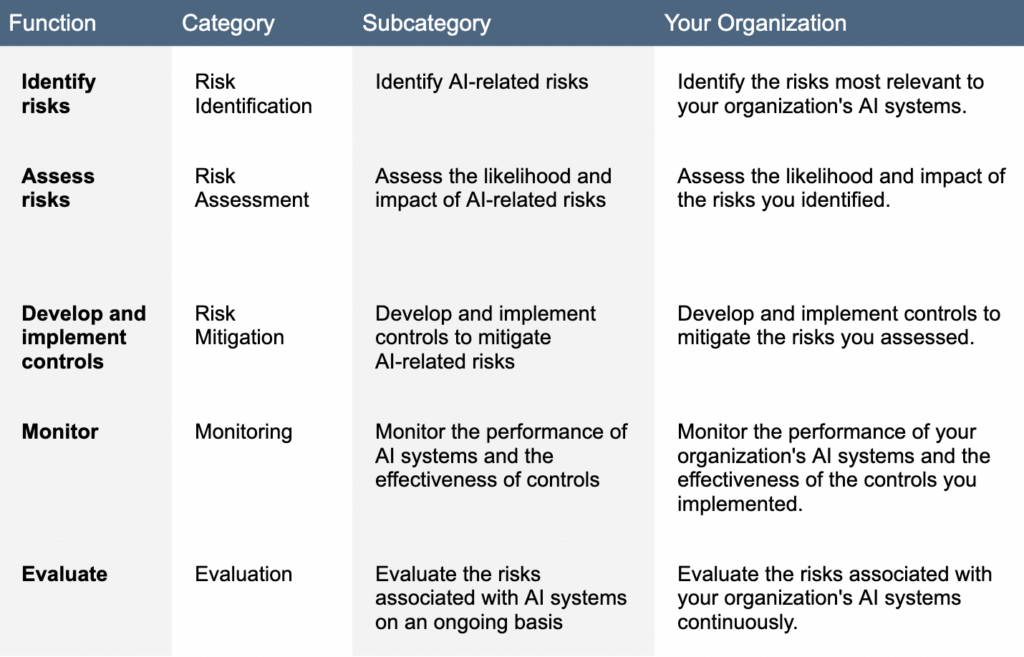
Organizations have a framework for evaluating their risk exposure to systems with AI. The framework provides a process for identifying and assessing risks, mitigating risks, monitoring risks, and responding to AI incidents.
How do you mitigate risk in AI-powered systems?
Organizations can use the following strategies to mitigate risk in AI-powered systems:
- Use secure development practices
- Implement security controls
- Train employees
- Conduct regular risk assessments
- Use AI responsibly
What 14 unique risks does NIST associate with AI?
Bias, Privacy, Security, Accountability, Explainability, Robustness, Safety, Sustainability, Fairness, Equity Transparency, Accountability, Governance.
What are the benefits of using RMF AI in risk management?
There are several benefits to using RMF AI in risk management, including increased efficiency, improved accuracy, mitigation against privacy violations, increased awareness of false outputs/errors, and reduced costs.
What are the challenges of using AI in risk management?
There are many challenges to using AI in risk management, including a lack of data, technical expertise, auditability & traceability, responsible development & use of AI capabilities, and interpretability (risks that are harder to identify).



